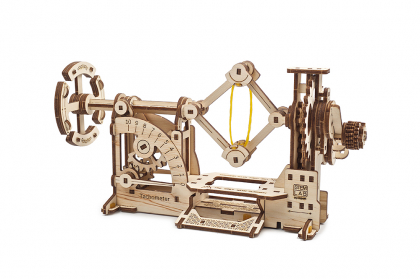
Tachometer educational mechanical model kit
Model size: 9.4*4.1*4.8 in (24*10.3*12.3 cm)
Package size: 8.1*7.4*2.5 in (20.5*18.8*6.3 cm)
Number of components: 133
Estimated time for assembly: 2,5 hours
Assemble the Tachometer and discover how it works.
- The model kit comes with a QR-code to the study guide about the mechanism, the principal of its working, the main characteristics, formulas. It also includes interesting assignments.
- Dive into augmented reality and look at how the Tachometer works. Interact with the model via a special AR application from Ugears.
Learn how the Tachometer works
A tachometer is a device designed to measure the rotational speed of various parts in engines and other mechanisms. It calculates revolutions per minute (RPM). The tachometer also measures and monitors load limits, in order to decrease or increase RPM so that the engine or mechanism runs within its optimal parameters.
Who invented the Tachometer, and when?
The tachometer was invented by the German engineer Dietrich Uhlhorn in 1817. His invention was a special device that measured centrifugal force. From 1840 on, this device has been used in railway locomotives, and later in cars and all manner of vehicular transport.
Use
The tachometer is used in mechanisms where it is necessary to accurately track RPM to avoid the negative consequences of overloads. Savvy motorists use tachometers to know when to shift gears (in cars with manual transmissions) and to control the load on the engine, thereby increasing the operating life of their vehicles.
What the Tachometer consists of and how it works
The Tachometer 3D puzzle from UGEARS' STEM Lab collection is a fully operational DIY wooden model of a tachometer, ready for you to assemble. When the handle is rotated, movement is transmitted through a reducer, increasing the RPM and displacing twin weights in the centrifugal unit. The higher the RPM, the more centrifugal force separates the weights, shifting a movable axle with flywheel. A pointer mechanism (dial) is fixed to the axle; the more the axle shifts (higher RPM), the more the dial arrow deflects, indicating higher speed rotation.
The Tachometer mechanism consists of:
- Handle
- Reducer
- Weights
- Axle
- Flywheel
- Dial
Connect the Tachometer to the Variator, creating a new mechanism
The Variator-Tachometer system demonstrates the direct relationship between the transmission ratio of a gearbox, and rotational speed.
When the handle of the Variator is rotated, the movement is transmitted through the reducer to the cone-shaped driving pulley. The rotation of the first cone is then transmitted through the belt to the other cone, which is the driven pulley. When the pedal attached to the housing is pressed, it shifts the fork holding the belt, thereby changing the rotational speed of the driven pulley. When the Tachometer is attached to the Variator, the changing rotational speed of the driven pulley of the Variator is transmitted to the Tachometer's reducer. This in turn will increase or decrease the centrifugal force on the weights, shifting the axle with flywheel. Shifting the axle deflects the indicator on the dial toward a higher or lower value. In this way, changes to the transmission ratio in the Variator will be seen to increase or decrease the RPM of the attached Tachometer.
The Variator-Tachometer mechanism consists of:
|
|
Ugears STEM puzzles are designed to suit different age groups with a special focus on learning component. The assembly of the model will be interesting and won’t take much time.
STEM Lab Model kits come with all you need in a box.
Just like the rest of Ugears wooden model kits, putting STEM Lab models together is fun and comprehensive: everything you need to build, learn, and discover comes in a box. There you will find:
- Wooden details pre-cut with a precise high-tech laser in high-quality plywood boards, as well as other materials required for assembly. DIY kits need no glue or additional instruments to build. The details come out of the board with a slight push.
- Step-by step illustrated instruction manual of 3D puzzles assembly.
- Practical Lab tasks with use of your model.
- QR-code to download a pocket study guide about the Ugears model, its mechanism, principle of its working, main characteristics, physical and mechanical formulas, and fun practical tasks.
- QR-code to download AR-application. Fascinating innovation from Ugears – new drive to learn more new things!